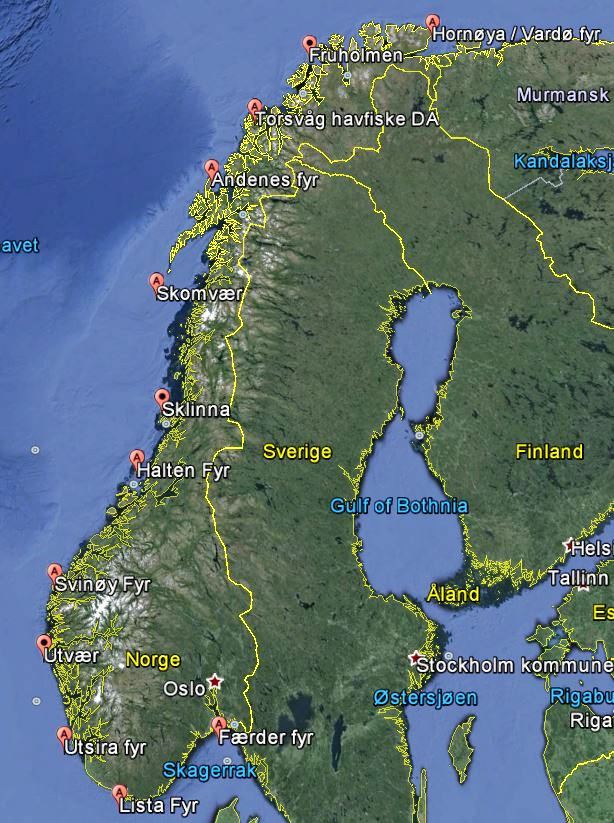
The DGPS service consists of 12 DGPS stations on the Norwegian coast. Each DGPS station has reference stations that monitor all visible satellites (over 8 degrees elevation) and calculates a correction value for each satellite. These corrections are transmitted over the Norwegian Coastal Administration's maritime radio beacon in the frequency band from 283.5 kHz to 315 kHz, and they can be received by users equipped with a DGPS radio beacon receiver. The user's GPS receiver uses the received corrections to improve the accuracy of the positioning it calculates.
Within the specified coverage area for the DGPS service, the user will achieve a positioning accuracy better than 10 metres (2 drms, 95 per cent probability).
Experience shows that the positioning accuracy is typically in the range of 1 to 3 metres.
In addition to improved positioning accuracy, the DGPS service will also provide integrity alarms for GPS. The DGPS service should have an availability of 99.5 per cent, calculated over a two-year period.
The DGPS service is linked to GPS. The Norwegian Coastal Administration, other Norwegian agencies or Norwegian authorities do not have any control over the technical and operational conditions for GPS.
Please be advised the DGPS-service will be discontinued in Norwegian waters from January 2026. More information here.